实例转换
0. 前言
InstaGAN Instance-aware image-to-image translation
Sangwoo Mo, Minsu Cho, Jinwoo Shin
github: https://github.com/sangwoomo/instagan
project: https://openreview.net/forum?id=ryxwJhC9YX
1. Introduction


整体分为三部分:
- an instance-augmented neural architecture
- a context preserving loss
- a sequential mini-batch inference/training technique
- an instance-augmented neural architecture: an image and the corresponding set of instance attributes.
- a context preserving loss: target instances and an identity function
- a sequential mini-batch inference/training technique: translating the mini-batches of instance attributes sequentially
2. InstaGAN
符号说明:
| 符号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| $\mathcal{X}$, $\mathcal{Y}$ | image domain |
| $\mathcal{A}, \mathcal{B}$ | a space of set of instance attributes |
| $\boldsymbol{a} = \lbrace ai \rbrace {i=1}^N $ | set of instance attributes |
| instance segmentation mask | |
| $G{XY}:\mathcal{X}->\mathcal{Y}, G{YX}:\mathcal{Y}->\mathcal{X}$ | tranlation function |
2.1 InstaGAN architecture
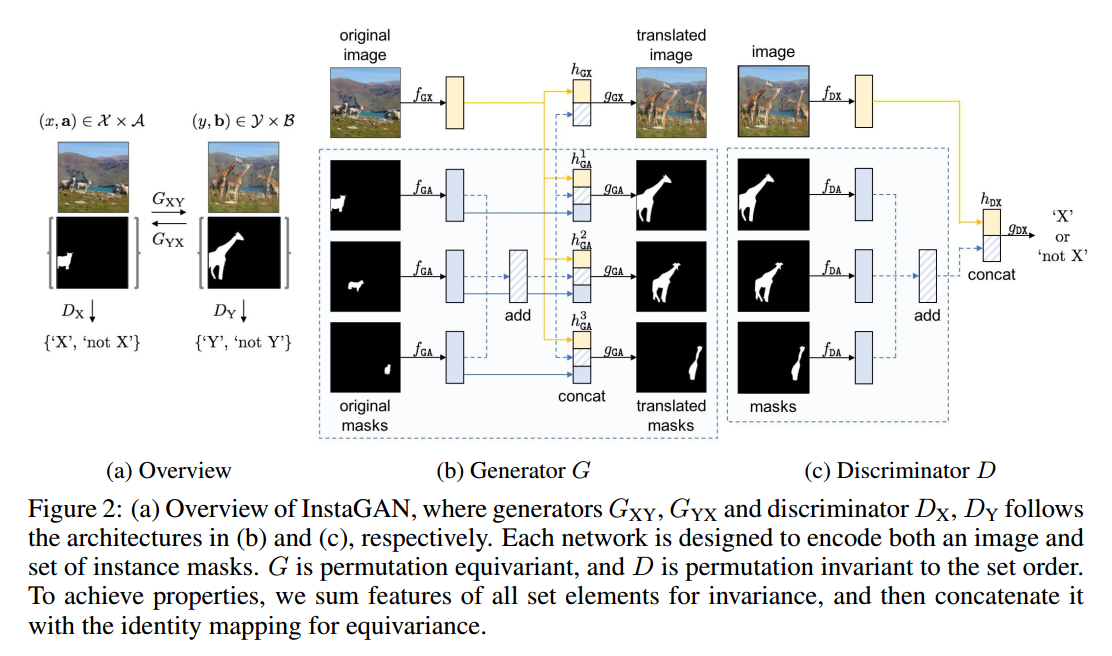

| 符号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| $f_{GX}$ | image feature extractor |
| $f_{GA}$ | attribute feature extractor |
| $H{GX}(x,a)=[f{GX}(x);\sum{i=1}^Nf{GA}(a_i)]$ | image representation |
| $H{GA}^n(x,a)=[f{GX}(x);\sum{i=1}^Nf{GA}(ai);f{GA}(a_n)]$ | image representation |
| $h{DX}(x,a)=[f{DX}(x);\sum{i=1}^Nf{DA}(a_i)]$ | image representation for discriminator |
| $f{GX},f{GA},f{DX},f{DA},g{GX},G{GA},G_{DX}$ | |
| $(x,a)->(y’,b’)$ | |
| $(y,b)->(x’,a’)$ |
作者为了能实现mask顺序不变性,采用相加的方式。
2.2 Training loss
- domain loss: GAN loss
- content loss: cycle-consistency loss and identity mapping loss and context preserving loss
LSGAN: 判断图片是原始的还是生成的
cycle-consistency loss: 循环一致性
identity mapping loss: 恒等映射
context preserving loss: 保留背景
其中,$w(a,b’), w(b,a’)$表示在原图片和生成图片都是背景的位置的权重是1.
Total loss:
2.3 sequential mini-batch translation
考虑到在图片上的实例可能很多,而GPU的所需空间随之线性增长,可能不符合现实情况,所以需要考虑在图片上可以转化一小部分实例。


符号说明:
| 符号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| $a=\cup_{i=1}^Ma_i$ | divide the set of instance masks a into mini-batch $a_1,a_2,…,a_M$ |
| $(xm, a_m)->(y’_m, b’_m) or (x{m+1}, a_{m+1})$ | mini-batch translation |
| $(y’_m, b’_{1:m})=(y’_m, \cup_{i=1}^m b’_i)$ | 用于判断真假 |
在这种情况下,不同的损失函数作用的范围发生改变,第m次时,content loss作用在$(xm, a_m), (y’_m, b’_m)$,domain loss 作用在$(x,a), (y’_m, b’\{1:m})$,即
- 每m个迭代detach一次,来使用固定大小的GPU。
- 划分mini-batch的原则:size of instances, 由大到小
3. experimental results
3.1 image-to-image translation results


通过上述结果的展示,我可以认为在这方面InstaGAN要比CycleGAN的效果更好,更能得到想要的指定的结果。
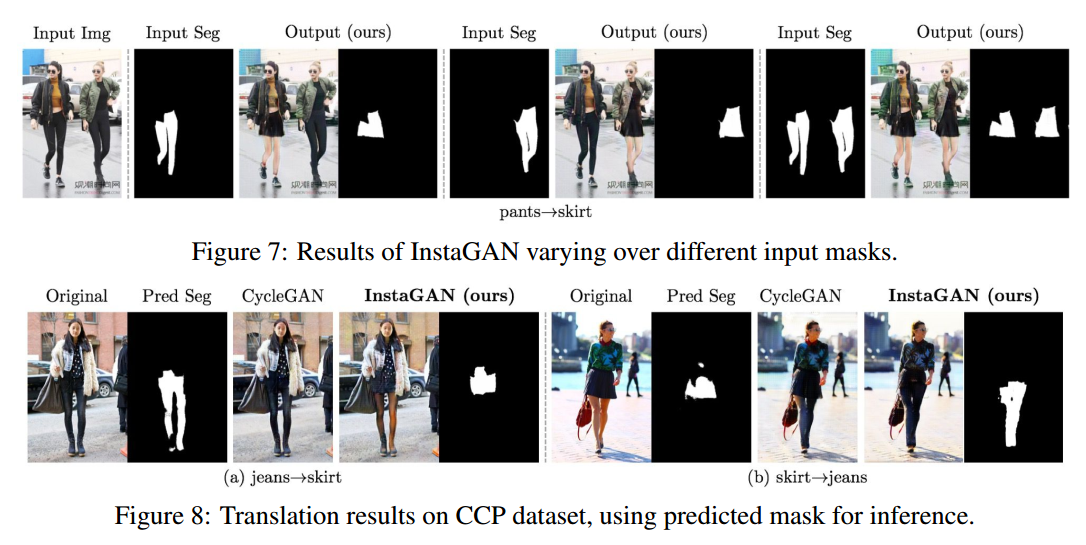


第一个结果表明可以通过控制掩码来控制生成的图片。
第二个结果表明可以使用预测的掩码进行转换图片,从而减少获取掩码的成本。
3.2 ablation study
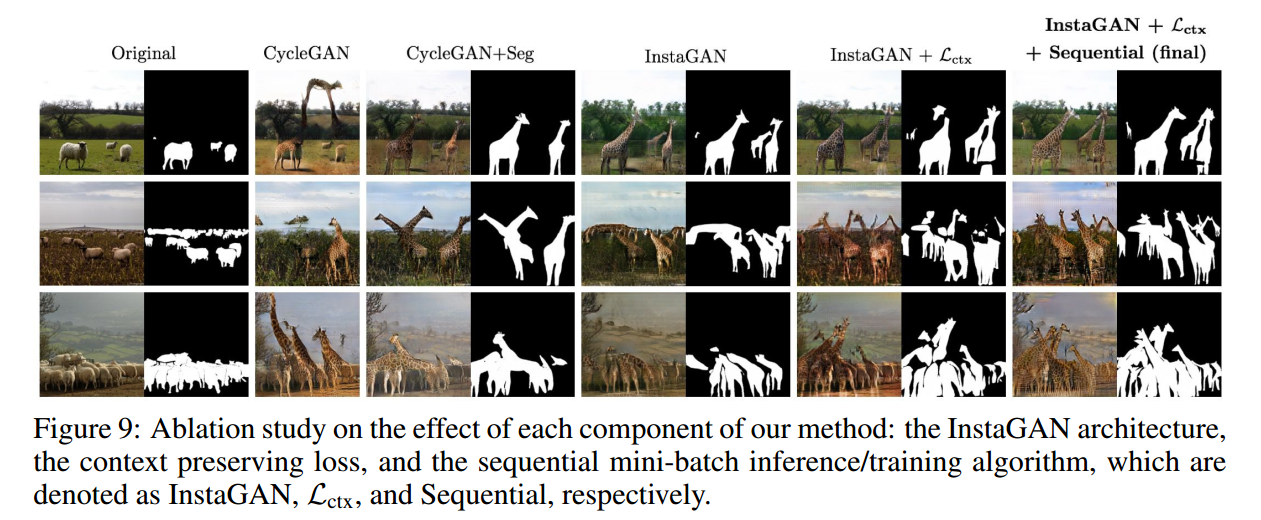

Fig.9 主要使研究作者提出的三部分功能的作用,instance mask,损失函数,mini-batch的影响,从效果上看,还是最后一张图片效果更好一些。
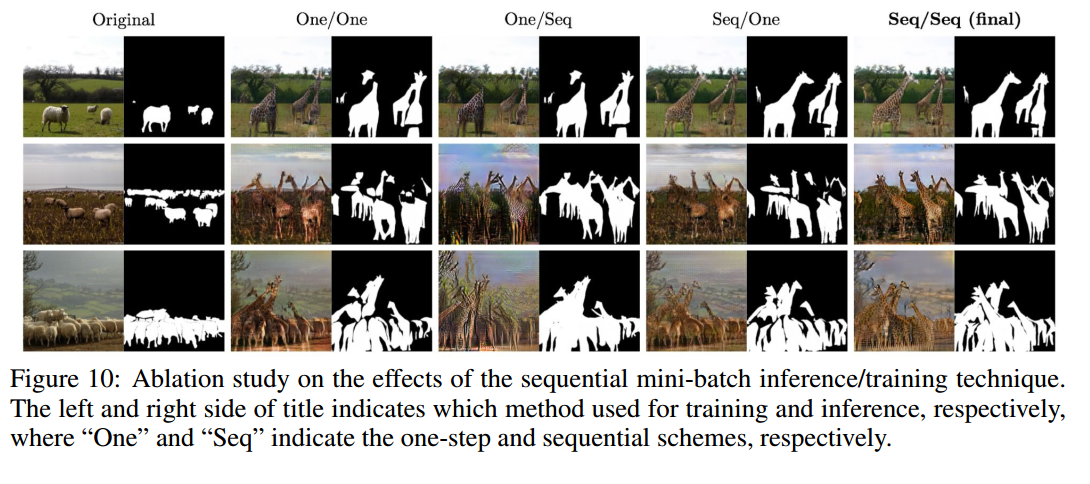

Fig.10分别表示在training和inference中使用one-step还是sequential方法,我觉得都差不多,但是对于有限的GPU是个很好的方法。
4. Appendix
4.1 architecture details
PatchGAN discriminator is composed of 5 convolutional layers, including normalization and non-linearity layers. We used the first 3 convolution layers for feature extractors, and the last 2 convolution layers for classifier.
4.2 traning details
- $\lambda{cyc}=10, \lambda{idt}=10, \lambda_{ctx}=10$
- Adam: $\beta_1=0.5, \beta_2=0.999$
- batch_size=4
- GPU = 4
- learning rate: 0.0002 for G, 0.0001 for D, 前m个epoch保持不变,后n个epoch线性衰减为0.不同的数据集的m和n不同
- size对于不同的数据集也不同。
4.3 trend of translation results


4.4 其他
我觉得这是相当于对于CycleGAN,加上了指向性生成,不再是单独地生成目标域风格的图片,而是对指定区域生成目标域风格的图片。
刚刚想到一个问题,InstaGAN可以生成指定形状的图片,但是对于同一形状的不同物体,比如生成红色的裙子和黑色的裙子这样子的任务,可能不行。
4.5 video translation results
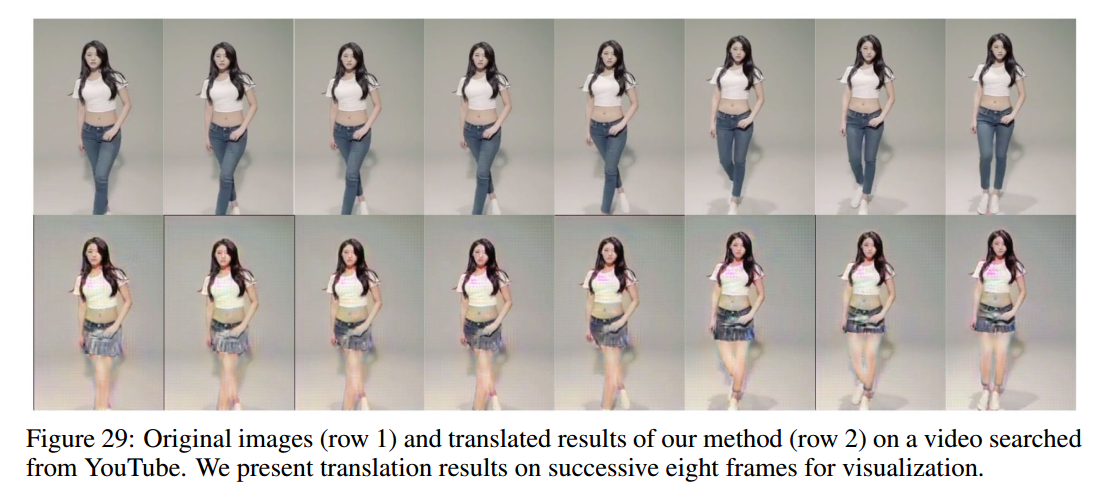


作者使用pix2pix作为分割。
感觉在视频上,裤子换成裙子后,能保持所有帧的裙子都是一样的,说明转换的稳定性很好。
5. code
看细节还是需要看代码的实现过程。
5.1 文件目录

通过文件组织,可以发现cycleGAN尽可能地考虑了可扩展性。
1 | . |
5.2 seg
从下面的代码可以看出,需要读取固定数量的instance的segmentation。
1 | # self.max_instances = 20 |
备注: 原始图片transforms之后,0~1变成了-1~1; 分割图片transforms之后-1表示背景,取值-1~1,这也是为什么补充的时候用-1补充的原因.
5.3 generator
ResNet generator is composed of downsampling blocks, residual blocks, and upsampling blocks. We used downsampling blocks and residual blocks for encoders, and used upsampling blocks for generators.
1 | class ResnetSetGenerator(nn.Module): |
5.4 Discriminator
On the other hand, PatchGAN discriminator is composed of 5 convolutional layers, including normalization and non-linearity layers. We used the first 3 convolution layers for feature extractors, and the last 2 convolution layers for classifier.
In addition, we observed that applying Spectral Normalization (SN) (Miyato et al., 2018) for discriminators significantly improve the performance, although we used LSGAN (Mao et al., 2017), while the original motivation of SN was to enforce Lipschitz condition to match with the theory of WGAN (Arjovsky et al., 2017; Gulrajani et al., 2017).
- [x] SpectralNorm 这个是怎么运行的? http://www.twistedwg.com/2018/10/13/SNGAN.html
虽然还是没有太搞懂其原理,但大致清楚了,是求矩阵的谱范数,因为难以求解,便用迭代的方式计算u、v。
1 | # Define spectral normalization layer |
5.5 model 的输入
1 | def set_input(self, input): |
前面说过,每次都生成20个mask,不足用-1补充,在输入网络时,只取面积最大的4个mask,然后对这4个进行或者从高到低排序或者随机排序。
1 | # ins_max = 4 |
这里的mask的合并没有太看懂,是为了去除(-1,1)之外的数字吗?
跑了代码,觉得是的,或许是担心有其他干扰因素吧,反正剩下的都是-1~1之间的数字.
1 | def merge_masks(self, segs): |
其他
- [ ] 这一步的意义是什么??
理解了,如果图片中没有instance,那么就不用进行下一步的转换了。
1 | self.forward_A = (self.real_A_seg_sng + 1).sum() > 0 # check if there are remaining instances |
- [x] fake_B_mul的意义是什么?
因为在sequential mini-batch translation中,GAN_loss是全局的,所以每次需要把之前的fake_B_seg_sng保存起来一起计算,因此每次的临时的self.fake_B_mul,而self.fake_B_seg_list保存是mini-batch计算得到的。
1 | if self.forward_A: |
- [x] 怎么选取的背景
只要在A中且在B中都是背景的则都算是背景,否则只要有instance的区域不为背景。
1 | def merge_masks(self, segs): |
1 | def merge_masks(self, segs): |
- [ ] 这里的empty的作用是什么
1 | empty = -torch.ones(self.real_A_seg_sng.size()).to(self.device) |
[ ] pix2pix 是怎么预测mask的,需要提前训练吗,数据集怎么提供?如果可以直接用,那么是否可以直接实现行人重识别的换人?
[x] 论文+代码,共4天